When it comes to roofing, the industry is filled with technical terms, jargon, and abbreviations that can be confusing for homeowners and even some professionals. Whether you’re planning a new roof installation, dealing with repairs, or simply trying to understand the lingo used by contractors, having a solid grasp of roofing terminology can make a big difference.
That’s why we’ve put together the Ultimate Glossary of Roofing Terms—your go-to resource for understanding everything from asphalt shingles to zinc strips. This comprehensive guide breaks down essential terms related to roofing materials, installation techniques, structural components, and maintenance tips. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to make informed decisions or a roofing pro sharpening your expertise, this glossary has you covered. Let’s dive in!
General Roofing Terms

- Roof Deck: The structural foundation of the roof, usually made of plywood or oriented strand board (OSB).
- Underlayment: A protective layer installed between the roof deck and the roofing material to prevent leaks.
- Flashing: Thin material, usually metal, used to prevent water penetration at roof joints and edges.
- Drip Edge: Metal flashing at the edges of the roof to direct water away from the fascia and into gutters.
- Fascia: A horizontal board along the edge of the roof that supports the gutter system.
- Soffit: The underside of a roof overhang that provides ventilation to the attic.
- Eaves: The lower edge of a roof that extends beyond the exterior walls.
- Ridge: The highest point of a roof where two sloping sides meet.
- Valley: The V-shaped channel where two roof slopes meet to allow water runoff.
- Hip: The external angle formed by the intersection of two sloping roof surfaces.
Types of Roofing

- Shingles: Individual overlapping pieces, often made of asphalt, wood, or metal, that cover a roof.
- Asphalt Shingles: The most common type of roofing material, most homeowners have shingle roofs in Minnesota made from a fiberglass or organic mat coated with asphalt. Learn more about asphalt shingles as an option for your home.
- Wood Shakes: Hand-split wooden shingles, often made from cedar.
- Metal Roofing: Roof panels made from steel, aluminum, or copper, known for durability. Available metal roofs in Arizona in Minnesota can include:
- Slate Roofing: Natural stone tiles used for premium and long-lasting roofing.
- Clay Tiles: Fired clay tiles commonly used in Mediterranean and Spanish-style homes.
- Synthetic Roofing: Man-made materials designed to mimic traditional materials like slate or wood.
- Roofing Felt: A layer of tar paper or synthetic material under shingles for extra protection.
- EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): A synthetic rubber roofing membrane used for flat roofs.
- TPO (Thermoplastic Polyolefin): A single-ply roofing membrane known for energy efficiency.
- PVC Roofing: A durable and weather-resistant roofing membrane for commercial and flat roofs.
Structural Components
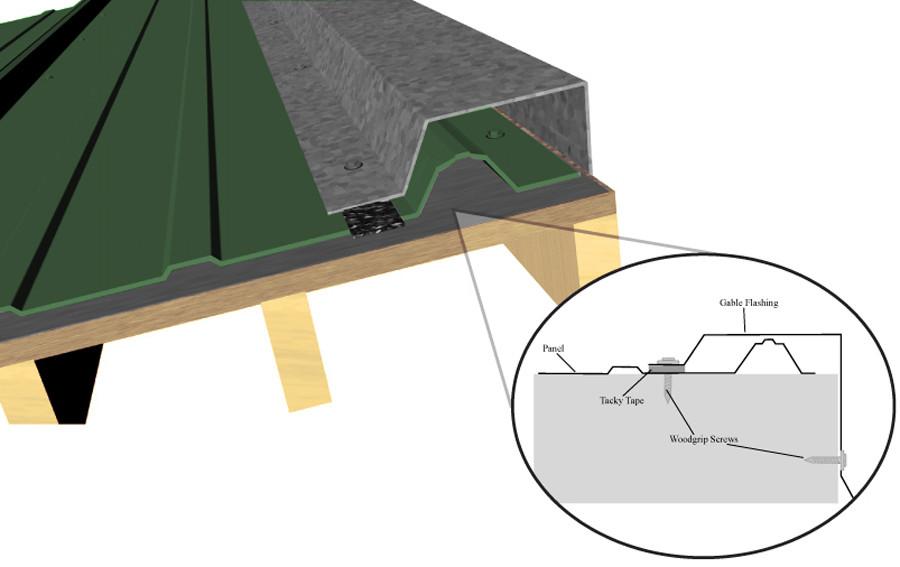
- Rafters: Sloped beams that support the roof deck and shingles.
- Trusses: Prefabricated triangular roof frames that provide structural support.
- Joists: Horizontal beams that support the weight of the roof and attic floor.
- Collar Ties: Horizontal beams that connect opposing rafters for structural stability.
- Purlins: Horizontal supports that reinforce metal roofing.
- Dormer: A protruding section of a roof containing a window, increasing attic space and light.
- Gable: The triangular upper part of a wall at the end of a pitched roof.
Roofing Systems and Features

- Cool Roof: A roof designed to reflect sunlight and absorb less heat.
- Green Roof: A roof covered with vegetation for insulation and environmental benefits.
- Flat Roof: A roof with little to no slope, commonly used in commercial buildings.
- Pitched Roof: A sloped roof that allows for water runoff. Learn more about roof pitches.
- Gambrel Roof: A symmetrical two-sided roof with two slopes on each side.
- Mansard Roof: A four-sided gambrel-style roof with a steep lower slope.
- Shed Roof: A single-sloped roof often used for modern designs.
- Parapet: A low wall at the edge of a flat roof.
Roofing Issues and Maintenance
- Ice Dam: A buildup of ice along the roof edge that prevents proper drainage.
- Blistering: Raised areas on shingles due to trapped moisture or heat.
- Granule Loss: The wearing away of the outer protective layer of shingles.
- Roof Leaks: Water intrusion caused by damage or poor sealing.
- Sagging Roof: A structural issue where part of the roof sags due to age or damage.
- Flashing Failure: When flashing deteriorates, causing leaks.
- Moss and Algae Growth: Organic growth that can damage shingles and reduce roof lifespan.
- Ventilation Issues: Poor airflow in the attic leading to moisture buildup and heat retention.
Installation and Repair Terms
- Tear-Off: The process of removing old roofing materials before a new installation.
- Re-Roofing: Installing a new roof over an existing one without removing old materials.
- Sealing: Applying a waterproof coating to prevent leaks.
- Nailing Patterns: The specific way shingles or roofing materials are nailed down.
- Overhang: The portion of the roof that extends beyond the walls.
- Gutter System: Channels and downspouts that direct water away from the roof and foundation.
Understanding roofing terminology helps homeowners make informed decisions and allows contractors to communicate clearly. Whether you’re planning on getting your roof replaced or have enough damage to request a free appointment to look at new options – knowing these terms will help you navigate the process with confidence.
Need professional advice? Schedule your free roofing appointment today!